Diamond and Gem Information
Diamond is the hardest material on Earth. This prevents it from being scratched and scuffed from any other material. Though it is the hardest it is not the toughest, and can still be fractured or chipped. Coloured stones vary in hardness and require special care in handling and storage.
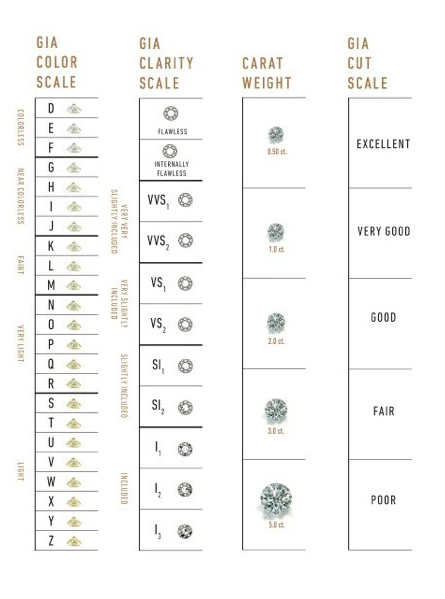
The value of a gemstone is determined by a grading system known as "the Four Cs". These are Carat-Weight, Clarity, Colour, Cut. This is most often referred to in the valuing of diamonds, but also applies to the grading and valuing of most coloured gemstones.
A chart displaying the Four Cs of diamond grading.
Image courtesy of GIA
Diamond, 14k white gold
The Four Cs
Carat-Weight
The size of a diamond is expressed in carats, as with all precious stones. The carat is 1/5 of a gram. For stone measurement a carat is divided into 100 "points". A half-carat diamond would be documented as a 0.50 ct, or could be referred to as a 50 point diamond. Cut diamonds commonly come in a range from 0.0025 ct and up.
Two stones of equal size can vary widely in their value and rarity, depending on the stone's colour and clarity. Size is an important factor when determining a diamond's value, but it is not the only consideration. However the value of high clarity, colourless diamonds increases dramatically for stones over 1.00 ct as they are very rare.
Clarity
Nearly all precious stones have clarity characteristics which are referred to as inclusions. Most are not visible without the aid of magnification and the fewer inclusions contained in a diamond, the higher its clarity grade and value in comparison to a similar stone if all other values are equal. Inclusions are not necessarily a negative however; no two stone's inclusions are alike and they can be thought of as the diamond's unique fingerprint. You can have a gemologist study and document your diamond's fingerprint so you have a record of your diamond's defining characteristics.
Colour
Diamonds are graded in a range from colourless to yellow or brown. Colourless diamonds allow white light to pass through, dispersing light in to rainbows which we see as the fire of a high quality diamond. Extremely rare diamonds displaying vivid colours in green, pink, red, and blue are known as "Fancies".Cut
Diamonds are cut into many different shapes, depending on the original structure of the rough stone. Different cuts will influence the diamond's sparkle and fire. People often confuse cut with the shape of a diamond. The cut refers to the number and alignment of facets on the diamond's surface. Shape is often a matter of the wearer's preference. Common shapes are round, oval, pear, marquis, emerald cut, ascher, trillion, princess.
Cut
Diamonds are cut into many different shapes, depending on the original shape of the rough stone. Differerent cuts will influence the diamond's sparkle and fire. People often confuse cut with the shape of a diamond. The cut refers to the number and alignment of facets on the diamond's surface. Shape is often a matter of the wearer's preference. Common shapes are round, oval, pear, marquis, emerald cut, ascher, trillion, princess.